
This specification conforms to FHIR®© R4
Governance for MedCom CareCommunication
- Coupling of messages
- Requirements for linebreaks
- Guidelines for the Use of SOR ID and Location Number (EAN)
- Requirements and optionality regarding the flow
- Acknowledgements
- Envelope
A CareCommunication can be send as a new message from a sender to a receiver. When a new message is sent, a message thread is started. A message thread is the correspondence being displayed to the user. A new message can be replied to or forwarded. Depending on the type of response or actions from the user, a new message thread might be created. Governance concerning when to create a new message thread will be accounted for in the following.
Governance for CareCommunication must be seen as additional requirements besides the Implementation Guide, use cases and clinical guidelines for application. Consequently, the requirements for managing message threads are also included in the test protocols.
Coupling of messages
A communication identifier is implemented to ensure that CareCommunications sent back and forth between healthcare professionals are displayed correct and likewise to the sender and receiver. When to create a new communication identifier is presented in section Requirements and optionality regarding the flow.
A Provenance instance describes the activity of the current message, for example is it a new message or a reply. In case the message is a reply or forwarding, the instance will reference the MessageHeader.id from the message it is responding to. Further, the Provenance instance includes a reference to the payload(s) (also known as the message segments with text or attachments) in the Communication instance that are included for this current message. If there, for example, is included one payload with message text and two with attachments for the current message, the Provenance will include the identifier from all three payloads.
Requirements for linebreaks
It is a requirement for the sender system to support the ability to include linebreaks in the free text field of the message.
It is a requirement for the receiver system to support and display linebreaks in the free text field of the message.
Linebreaks must be inserted in the free text by using \n in FHIR-JSON and 
 in FHIR-XML.
Use of SOR ID and Location Number (EAN)
Clear communication in CareCommunication relies on understanding how the SOR ID and location number (EAN) are used. In the FHIR profile for CareCommunication medcom-messaging-organization, it is required that both the SOR ID and the location number are specified for the organization sending/receiving a CareCommunication. This means: 1) Senders must be registered with a SOR ID that has an associated location number. 2) If a sub-department does not have a location number linked to its SOR ID, CareCommunications from this sub-department must be sent from the overarching organizational level where both a SOR ID and a location number are associated.
Requirements and optionality regarding the flow
Rules regarding new CareCommunication
Sender system
| Rule name | Rules to contrain the use of new CareCommunications |
|---|---|
| medcom-carecommunication-1 | User of a sender system SHALL be able to send a new CareCommunication. The sender system SHALL include a unique communication identifier for the message thread. |
Receiver system
| Rule name | Rules to contrain the use of new CareCommunications |
|---|---|
| medcom-carecommunication-2 | User of receiver systems SHALL be able to see a new CareCommunication is received in a new message thread. |
Rules regarding replies
It is a requirement that a system can send a reply to an already received CareCommunication, which can be a new message, reply or forwarding. It is also a requirement that a system can receive and display all message segments in the message to create a historical overview for the user. Figure 1 illustrates the flow for replying with CareCommunications.
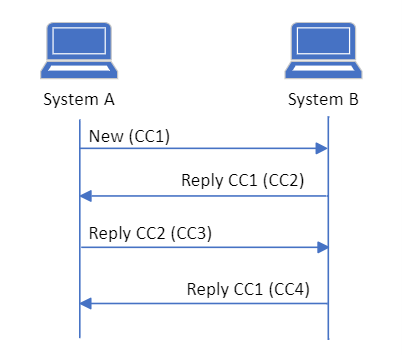
Sender system
| Rule name | Rules to contrain the use of reply CareCommunications |
|---|---|
| medcom-carecommunication-3 | User of a sender system SHALL be able to reply to a new CareCommunication or the latest received reply or forwarded CareCommunication. In these cases, the communication identifier SHALL remain the same in the reply. |
| medcom-carecommunication-4 | User of a sender system SHOULD be able to reply to the latest message when the latest message is sent from the sender system itself. |
| medcom-carecommunication-5 | User of the sender system SHALL NOT be able to reply to messages which isn’t the latest. If this is necesary, a new message thread with a unique communication identifier SHALL be created. |
| medcom-carecommunication-6 | When replying to a CareCommunication that already includes an attachment, the base64-encoded content SHALL NOT be included, but the identifier, timestamp and title SHALL be included, and author information SHALL be included if available. |
| medcom-carecommunication-7 | When replying to a CareCommunication with a specific sender, the specific sender SHALL automatically set the specific sender as the specific recipient in the reply. |
Receiver system
| Rule name | Rules to contrain the use of reply CareCommunications |
|---|---|
| medcom-carecommunication-8 | User of receiver system SHALL be able to see the received replies in the same message thread as previous CareCommunication with identical communication identifier. |
| medcom-carecommunication-9 | In cases where a CareCommunication does not arrive and an unknown message segment is afterwards included in a received CareCommunication, the unknown message segment SHALL be displayed to the user in the associated message thread. The messages SHALL be ordered by the timestamp from the message segment. It SHALL be clear to the user that an unread message is received. |
| medcom-carecommunication-10 | In cases where a CareCommunication arrives in unexpected order the received messages SHALL be displayed to the user in the associated message thread, ordered by the timestamp from the message segment. When a delayed CareCommunication appears, it SHALL be displayed in the same message thread. It SHALL be clear to the user that an unread message is received. |
| medcom-carecommunication-11 | In cases where a reply is received with an unknown communication identifier, the message segment(s) SHALL be displayed to the user in a new message thread. |
| medcom-carecommunication-12 | When two systems, at the same time, sends a reply to the same CareCommunication with the same communication identifier, both systems SHALL be able to handle receiving a reply which is not the latest reply in the message thread in the system. This is managed by including the received CareCommunication in the message thread with the same communication identifier. The flow for parallel sent CareCommunications is illustrated on Figure 2. It SHALL be clear to the user that an unread message is received and which message it is a reply to. If the time stamps in the message segments with the message text are different, the messages SHALL be ordered by these and if they are identical the message segments SHALL be ordered by the sender of the messages. The message sent by the initiator of the communication SHALL appear as the first, followed by the message send by the replier. In both case no other changes MUST be applied to the message segment or Provenance instances. |
| medcom-carecommunication-13 | The user SHALL be able to continue the communication in the message thread after the flow of messages received in 9, 10, 11, and 12. |
Note: For the scenarios (9, 10 and 11) the handling in the receiver system is the same: A) create a new message thread if the communication identifier is unknown or if known, include the message in the message thread with an identical communication identifier, B) order the messages based on the time stamp in the message segment, and C) make it clear to the user that an unread message is received.
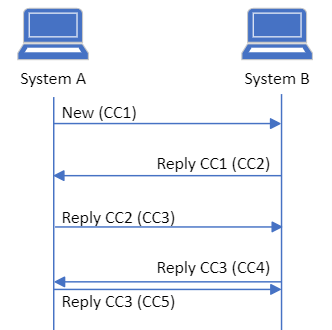
Rules regarding forwarding
It is optional for the system to support forwarding of a CareCommunication; however, it is a requirement that all systems can receive and display a forwarded CareCommunication. If the sender system supports forwarding the user must be able to forward the entire message thread which may consist of one or more CareCommunications and attachments. System functionality where the user may choose and select which specified parts of the message thread that the user wishes to forward, is not required but optional. Only the chosen message segments and associated Provenances must be included. The flow of forwarded CareCommunications can be seen in Figure 3.
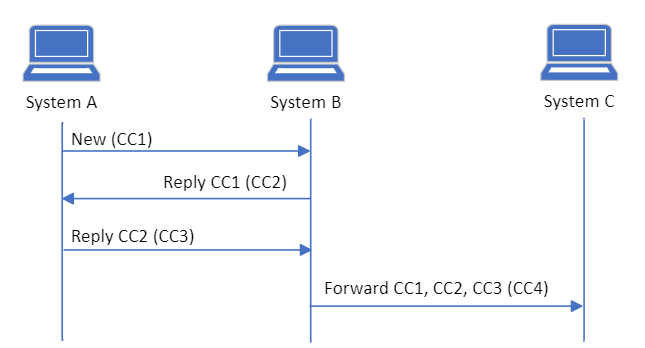
Sender system
| Rule name | Rules to contrain the use of forwarding CareCommunications |
|---|---|
| medcom-carecommunication-14 | User of sender system SHOULD be able to forward all CareCommunication in a message thread, as illustrated in Figure 3. In this case, the forwarding SHALL include all previous message segments and the sender system SHALL create a new message thread with a new, unique communication identifier. |
| medcom-carecommunication-15 | User of sender system SHOULD be able to forward the latest sent or received CareCommunication or a previously sent or received CareCommunication. If the user forwards and choose specific parts of the message, only the selected parts SHALL be included, meaning the associated message segment(s) and Provenances. It is not allowed only to removed attachment(s), as this will cause the references to the payload in the Provenance to be incorrect. |
| medcom-carecommunication-16 | After forwarding a CareCommunication, the user SHALL be able to continue the communication in the original message thread. |
Receiver system
| Rule name | Rules to contrain the use of forwarding CareCommunications |
|---|---|
| medcom-carecommunication-17 | Receiver system SHALL be able to display the forwarded CareCommunication in a new message thread. All content in the CareCommunication SHALL be displayed in the new message thread. |
| medcom-carecommunication-18 | The user SHALL be able to reply to a forwarded CareCommunication but SHALL NOT reply to one of the previous message segments included in the forwarding. |
| medcom-carecommunication-19 | If the system receives a forwarding, the user MAY forward this to a new receiver. In this case, the forwarding SHALL include all previous message segments and the sender system SHALL create a new message thread with a new, unique communication identifier. |
General rules
Sender system
| Rule name | General rules to contrain the use of CareCommunications |
|---|---|
| medcom-carecommunication-20 | Sender system SHALL be able to receive and connect Acknowledgements to send CareCommunications and handle negative Acknowledgements. |
| medcom-carecommunication-21 | Sender system SHALL be able to handle communication identifier as stated above and add message segments and Provenance instances in a CareCommunication. |
Receiver system
| Rule name | General rules to contrain the use of CareCommunications |
|---|---|
| medcom-carecommunication-22 | Receiver system SHALL be able to acknowledge a received CareCommunication with an Acknowledgement. The Acknowledgement SHALL include the latest Provenance from the CareCommunication and a new Provenance for the Acknowledgement. |
| medcom-carecommunication-23 | Receiver system SHALL display the messages in timely order based on the timestamp in the message segments. |
Acknowledgements
| Rule name | General rules to contrain the use of Acknowledgement |
|---|---|
| medcom-carecommunication-24 | All MedCom FHIR messages SHALL be acknowledged. To acknowledge a CareCommunication message the MedCom FHIR Acknowledgement standard SHALL be used. |
Envelope
| Rule name | Rules to contrain the use of VANSEnvelope |
|---|---|
| medcom-carecommunication-25 | Since the CareCommunication message is sent over the VANS-network, it SHALL be wrapped in a VANS-envelope. This page describes the use of VANS-envelope. |
| medcom-carecommunication-26 | Values of fields used in a VANSenvelope SHALL obey to the specifications described on the page for VANSenvelope for a CareCommunication message. |
About
Support or contact
MedCom is responsible for this page. If you have any questions regarding this page, please contact fhir@medcom.dk or write to MedComs stream on Zulip.Version of this documentation
The version of this documentation is: Version 2.0.2 You can finde the release note of the version here."FHIR® is the registered trademark of HL7 and is used with the permission of HL7. Use of the FHIR trademark does not constitute endorsement of this implementation guide by HL7, nor affirmation that this content is conformant to the various applicable standards"